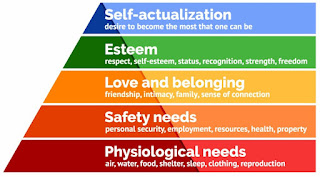
Maslow's Hierarchy of Need
Maslow's Hierarchy of Need
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in Psychological Review. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity.
Physiological Needs
The basic physiological needs are probably fairly apparent—these include the things that are vital to our survival. Some examples of physiological needs include:Food, Water, Breathing, Homeostasis
In addition to the basic requirements of nutrition, air and temperature regulation, the physiological needs also include such things as shelter and clothing. Maslow also included sexual reproduction in this level of the hierarchy of needs since it is essential to the survival and propagation of the species.
Security and Safety Needs
As we move up to the second level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, the requirements start to become a bit more complex. At this level, the needs for security and safety become primary. People want control and order in their lives, so this need for safety and security contributes largely to behaviors at this level.Some of the basic security and safety needs include:Financial security, Heath and wellness, Safety against accidents and injury, Finding a job, obtaining health insurance and health care, contributing money to a savings account, and moving into a safer neighborhood are all examples of actions motivated by the security and safety needs. Together, the safety and physiological levels of the hierarchy make up what is often referred to as the basic needs.
Social Needs
The social needs in Maslow’s hierarchy include such things as love, acceptance, and belonging. At this level, the need for emotional relationships drives human behavior. Some of the things that satisfy this need include:Friendships, Romantic attachments,Family,Social groups,Community groups,Churches and religious organizations
In order to avoid problems such as loneliness, depression, and anxiety, it is important for people to feel loved and accepted by other people. Personal relationships with friends, family, and lovers play an important role, as does involvement in other groups that might include religious groups, sports teams, book clubs, and other group activities.
Esteem Needs
At the fourth level in Maslow’s hierarchy is the need for appreciation and respect. When the needs at the bottom three levels have been satisfied, the esteem needs begin to play a more prominent role in motivating behavior.At this point, it becomes increasingly important to gain the respect and appreciation of others. People have a need to accomplish things and then have their efforts recognized.
In addition to the need for feelings of accomplishment and prestige, the esteem needs include such things as self-esteem and personal worth. People need to sense that they are valued and by others and feel that they are making a contribution to the world. Participation in professional activities, academic accomplishments, athletic or team participation, and personal hobbies can all play a role in fulfilling the esteem needs.
People who are able to satisfy the esteem needs by achieving good self-esteem and the recognition of others tend to feel confident in their abilities. Those who lack self-esteem and the respect of others can develop feelings of inferiority.Together, the esteem and social levels make up what is known as the psychological needs of the hierarchy.
Self-Actualization Needs
At the very peak of Maslow’s hierarchy are the self-actualization needs. "What a man can be, he must be," Maslow explained, referring to the need people have to achieve their full potential as human beings.According to Maslow’s definition of self-actualization:"It may be loosely described as the full use and exploitation of talents, capabilities, potentialities, etc. Such people seem to be fulfilling themselves and to be doing the best that they are capable of doing... They are people who have developed or are developing to the full stature of which they capable."Self-actualizing people are self-aware, concerned with personal growth, less concerned with the opinions of others, and interested fulfilling their potential.


Comments
Post a Comment